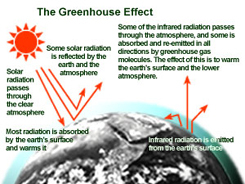
The greenhouse effect is the rise in temperature that the Earth experiences because certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) trap energy from the sun. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60ºF colder. Because of how they warm our world, these gases are referred to as greenhouse gases.
How the Greenhouse Effect Works
Have you ever seen a greenhouse? Most greenhouses look like a small glass house. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, especially in the winter. Greenhouses work by trapping heat from the sun. The glass panels of the greenhouse let in light but keep heat from escaping. This causes the greenhouse to heat up, much like the inside of a car parked in sunlight, and keeps the plants warm enough to live in the winter.
The Earth’s atmosphere is all around us. It is the air that we breathe. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere behave much like the glass panes in a greenhouse. Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, passing through the blanket of greenhouse gases. As it reaches the Earth's surface, land, water, and biosphere absorb the sunlight’s energy. Once absorbed, this energy is sent back into the atmosphere. Some of the energy passes back into space, but much of it remains trapped in the atmosphere by the greenhouse gases, causing our world to heat up.
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gasses include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), halogenated fluorocarbons (HCFCs) , ozone (O3), perfluorinated carbons (PFCs), and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
See Global Warming
 Print
Print Email
Email